Versal ACAP Platform & Power Management
Industry Focus Towards Getting Maximum Performance with Optimum Power
With the latest evolution, performance per watt of power usage has become critical for any SoC. SoC designers are striving for energy conservation to manage the ultimate trade-off between power consumption and differentiating performance. Of greater importance are the application processors where a mere milliwatt of power consumption can make the difference between design win in the market-leading application or losing an opportunity to participate in the rapid growth market. SoC Power Management is gaining prominence in several traditional markets ranging from data center CPUs, automotive infotainment systems to IoT devices and wearables. In today’s world, SoCs are ideally expected to support a variety of use cases with optimum power levels.
Design Choices and Power Management Techniques in Complex SoCs
While CPUs, GPUs, and peripherals dominate SoC’s power management attention, other functional blocks are often overlooked. Today, interconnect technologies for accelerators & FPGA PLs also gain prominence in the SoC space with rising data center and cloud-oriented use-cases. More significant advantages have been realizable for those who have switched over to advanced Network-On-Chip (NoC) interconnect fabrics. Essential benefits of NoC are managing power consumption across different functional blocks of the SoC and the interconnects between them, not just the CPU and GPU. Since the interconnect links all major available blocks, it provides an excellent opportunity to enhance best power management practices:
- Dynamic frequency and voltage scaling
- Data path optimization
- Different power islands
- Clock gating
- Adaptive voltage scaling
- Standby/leakage current management
Thus, NoC brings in a lot of advantages compared to older bus & crossbar interconnect technologies. To leverage the power management strengths of the NoC, SoCs will need a dedicated unit that can manage all the different resources depending on the application’s requirements, like Xilinx Versal ACAP’s PLM unit and ZynqMP Ultrascale+ MPSoC’s PMUFW unit.
Power management in Xilinx Versal ACAP
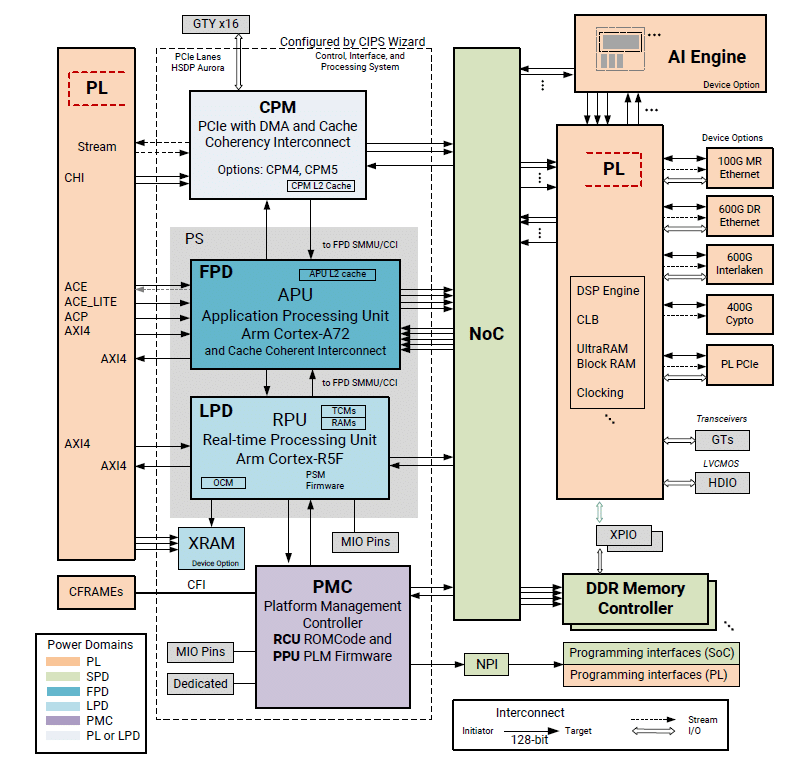
Source: Xilinx
Xilinx Versal ACAP has functional blocks in different power domains like LPD, FPD, PL, NoC, PMC, etc.
FP domain
Full Power Domain (FPD) is responsible for consuming high power. It mainly consists Cortex-A72 application processor for running a heavy application like Linux. It also has another high-power component like GPU, DP, PCIe, etc.
LP domain
Low Power Domain (LPD) mostly consists of small low-power peripherals like I2C, SPI, UART, etc. It also includes a cortex-R5 processor for running safety/secure/RTOS applications and on chip memories like OCM, TCM for faster memory access. This domain is also responsible for housing wakeup sources like UART, Ethernet, USB, etc.
PL domain
Programmable Logic (PL) domain includes DSP engine, Configurable logic block (CLB), Block RAM, Ultra RAM, and AI Engine blocks. This provides the improved application performance of the overall embedded system design.
NoC domain
The Network on Chip (NoC) provides the interconnects for the entire SoC units. It provides the connection between master and slave on an AXI4-based network and maps the global address space based on NoC interconnect.
PMC domain
Platform Management Controller (PMC) runs platform management firmware, which provides the platform management for the entire ACAP. The firmware running on PMC can manage the peripherals and power domains depending upon the user applications.
The power numbers of ACAP ranges from hundreds of watts to microwatts depending on the configuration. The individual power domains can be entirely powered down so that its power requirement, including static power, becomes virtually zero. Xilinx provides extensive software support for Power Management in the U-boot, ATF, Xen, Linux, and the BareMetal application.
MosChip, with its rich experience in Platform Management on Xilinx Ultrascale+ MPSoC, was one of the early entrants into Versal ACAP platform management, supporting Xilinx extensively in developments across software layers in ATF, Xen, Linux, and BareMetal level. Going further, MosChip has scaled up to keep some of the key end-customers of Xilinx.
Some of the key features implemented in power management on Versal ACAP by MosChip are:
Linux suspend/resume with different wakeup sources
- APU (Cortex-A72 runs Linux on the Versal ACAP can configure different peripherals such as UART, Ethernet (Wakeup on LAN), USB, etc. The Platform Management Controller (PMC) has been configured to handle multiple wake-up sources appropriately activated when the user suspends the system. This allows a complete power down of the Full Power Domain (FPD) domain.
- When the wakeup source device generates a wakeup event, PMC gets the interrupt and powers up the FPD and APU running Linux.
- Xilinx’s Versal ACAP is a differentiating platform that will transform the horizon of power-hungry applications while smartly conserving energy and ensuring the best performance. MosChip aims to continue playing key roles with its highly skilled talent pool to enable end-to-end solutions, leveraging Versal ACAP advancements in platform and power management.
About MosChip:
MosChip has 20+ years of experience in Semiconductor, Embedded Systems & Software Design, and Product Engineering services with the strength of 1300+ engineers.
Established in 1999, MosChip has development centers in Hyderabad, Bangalore, Pune, and Ahmedabad (India) and a branch office in Santa Clara, USA. Our embedded expertise involves platform enablement (FPGA/ ASIC/ SoC/ processors), firmware and driver development, BSP and board bring-up, OS porting, middleware integration, product re-engineering and sustenance, device and embedded testing, test automation, IoT, AIML solution design and more. Our semiconductor offerings involve silicon design, verification, validation, and turnkey ASIC services. We are also a TSMC DCA (Design Center Alliance) Partner.
Stay current with the latest MosChip updates via LinkedIn, Twitter, FaceBook, Instagram, and YouTube
Author
-

Mustaqh Ali Shaik is a versatile Digital Marketing Manager at MosChip with over a decade of experience driving brand growth for technology companies and serving as Marketing Chair for international conferences like IESA and VLSID, IEEE. Skilled in SEO, SEM, email marketing, WordPress, social media, and content strategy, he is a results-driven leader, mentor, and lifelong learner known for delivering strong digital presence and sustainable growth with zero investment.